What is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)?
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a form of psychotherapy that focuses on the connection between our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. It’s based on the idea that our thoughts and perceptions about situations influence how we feel emotionally and how we behave in response.
The CBT Cycle:
- Thoughts: In CBT, we recognize that our thoughts are not always accurate reflections of reality. Sometimes, we have automatic negative thoughts or cognitive distortions that lead to negative emotions and behaviors
- Feelings: Our thoughts directly impact how we feel. If we have negative or irrational thoughts, we are likely to experience negative emotions such as sadness, anxiety, or anger.
- Behaviors: Our feelings then influence how we behave. For example, if we’re feeling anxious, we might avoid certain situations or engage in safety behaviors. These
behaviors can reinforce our negative thoughts and maintain the cycle of distress.
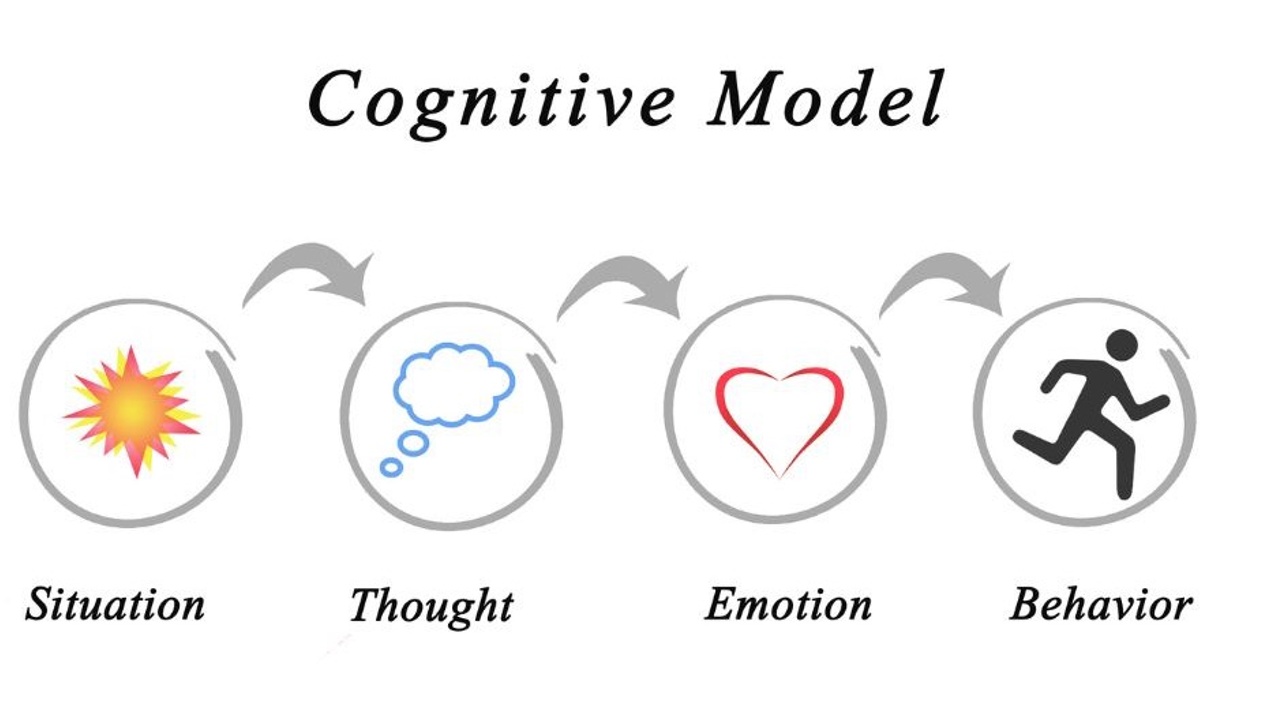
How Thoughts Affect Feelings and Behavior:
- Example: Let’s say you’re invited to a social event. If your automatic thought is, “I’ll embarrass myself,” you might feel anxious or self-conscious. As a result, you might avoid the event altogether (behavior), which reinforces the belief that social situations are threatening.
- Alternative: If we challenge and replace that thought with, “I can handle social situations,” you might feel more confident and motivated to attend the event. Over time, facing social situations will become easier, and your confidence will grow.
How Does CBT Work?
- Identifying Patterns: In therapy, we work together to identify patterns of thinking and behavior that contribute to your distress. We pay attention to automatic thoughts—those quick, reflexive thoughts that pop into your mind in response to situations.
- Challenging Thoughts: Once we’ve identified these patterns, we examine them closely to determine their accuracy and helpfulness. We ask questions like, “Is there evidence to support this thought?” or “What would I say to a friend in this situation?”
- Replacing with Balanced Thoughts: We then work to replace negative or distorted thoughts with more balanced and realistic ones. This process, known as cognitive restructuring, helps you develop a more adaptive way of thinking.
- Behavioral Changes: Alongside addressing your thoughts, we also focus on making behavioral changes. This might involve gradually facing feared situations (exposure), learning new coping skills, or practicing relaxation techniques.
- Practice and Homework: Between sessions, you’ll practice the skills and techniques learned in therapy through homework assignments. This helps reinforce what you’ve learned and promotes lasting change.
- Monitoring Progress: Throughout therapy, we’ll monitor your progress and make adjustments as needed. We’ll celebrate successes and troubleshoot any challenges that arise along the way.
In Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, we explore the connection between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors to help you break free from negative patterns and live a more fulfilling life. By challenging and changing unhelpful thoughts and behaviors, you can experience significant improvements in your emotional well-being and overall quality of life. If you’re interested in learning more about CBT or have any questions, feel free to discuss them with your therapist. Together, we’ll work collaboratively to help you achieve your therapy goals.



